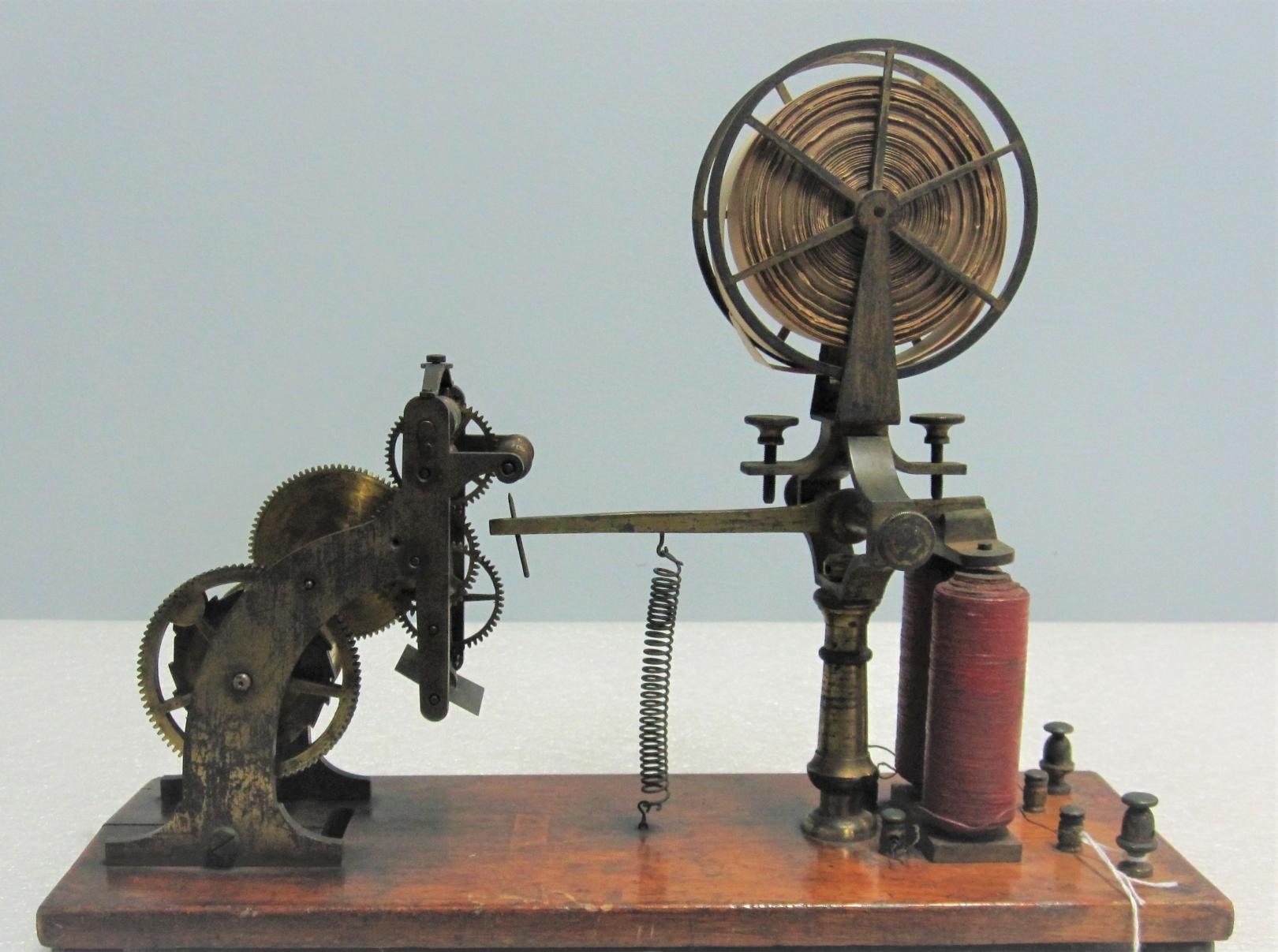
Telegraph Register (FI Cat.#75-3-14) The Franklin Institute Collection
Date:
Origins of the Telegraph
For centuries, people tried to find ways to communicate across long distances quickly. Flags, sounds, smoke, or lights would only go as far as they could be seen or heard. While the idea for a machine dates back to the 1700s, it wasn’t until the 19th century that the telegraph – a machine that transmits text across distance – was developed. While many inventors came up with different versions, the man who truly brought the telegraph to the world is Samuel Morse.
Morse began working on his version of the electric telegraph in the 1830s. He started his career as a painter, and was a successful artist. While he was away from home working on a commission, his wife died suddenly. Because of how far away he was, by the time he found out, she had already been buried. Morse felt firsthand the need for a quick way to send news. Later, while on a ship, he overheard fellow passengers discussing electromagnetism, which gave him the idea for how a telegraph might work.
Morse Code
One of Morse’s greatest contributions to telegraphy was Morse code, a system of using dots and dashes to represent characters in a text, making it faster and easier to transmit messages by simplifying what was actually transmitted. Morse’s system was also simpler in that it used a single wire, rather than multiple wires, to transmit the signals.
Morse demonstrated his work for Congress in 1838, and received federal funding in the early 1840s. With this funding, Morse connected Washington, DC and Baltimore, a distance of 40 miles. On May 24, 1844, Morse sent the first telegraph across this line: “What hath God wrought?” It would be the first of many transmissions to come.
The Impact
The electric telegraph changed the way people communicated. It helped the newly-built railway system coordinate schedules, and helped the White House strategize during the Civil War by providing access to information about the troops that had not been available before. The telegraph also allowed ordinary people to connect with loved ones far away. Although the telegraph faded from use in the 20th century in favor of newer technologies like the telephone and internet, it had a huge impact on society.
Interested in learning more? Check out our Ingenious: The Evolution of Innovention video series!
Sources:
Library of Congress
Elon.edu


